Until recently, website owners did not need to worry about taking extra measures to secure their web pages.
It used to be that only the medical and banking industry had to protect their data, but times have quickly changed all this!
Google has officially recommended securing websites to not only protect visitors and website owners but to ensure your websites performs well in search.
If your website is unsecured, it may easily be compromised. Your customer's data could be stolen, which, in turn, will lead to lost revenue and costly coding repairs and other issues.
As companies and organizations offer more online services and transactions, internet security has become a priority and a necessity for all online transactions.
To keep customer information private and secure, companies and organizations need to add SSL certificates to their websites to enable secure online transactions.
What is SSL?
SSL security is a similar concept to the big blue USPS mailbox at your local post office. Anyone can drop mail in the mailbox, but once inside, only official postal workers may access it with a special key.
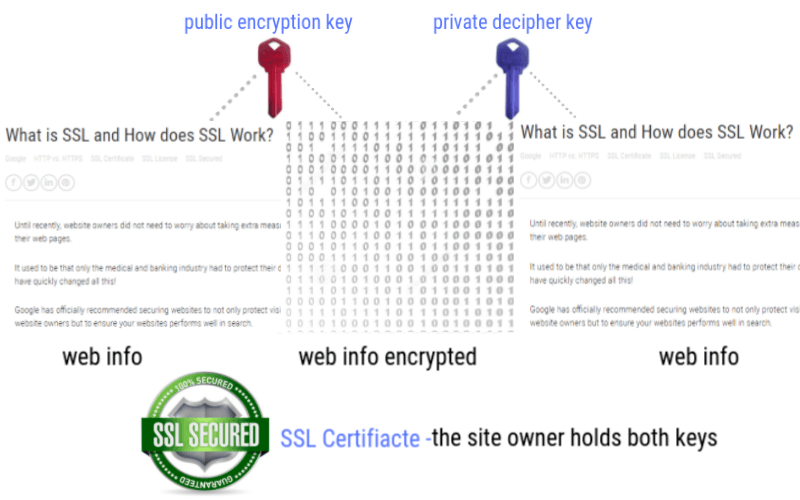
For an SSL Certificate to function properly, these three must work together: Public Keys, Private Keys, and the SSL Certificates.
An SSL certificate verifies that the website is a legitimate business and that it's safe to conduct business online.
Regardless of the type of business you have, the security of your web domain needs to be as secure as your home, your business, or bank account.
To understand the impact of switching from HTTP to HTTPS, first, let’s talk about what they are.
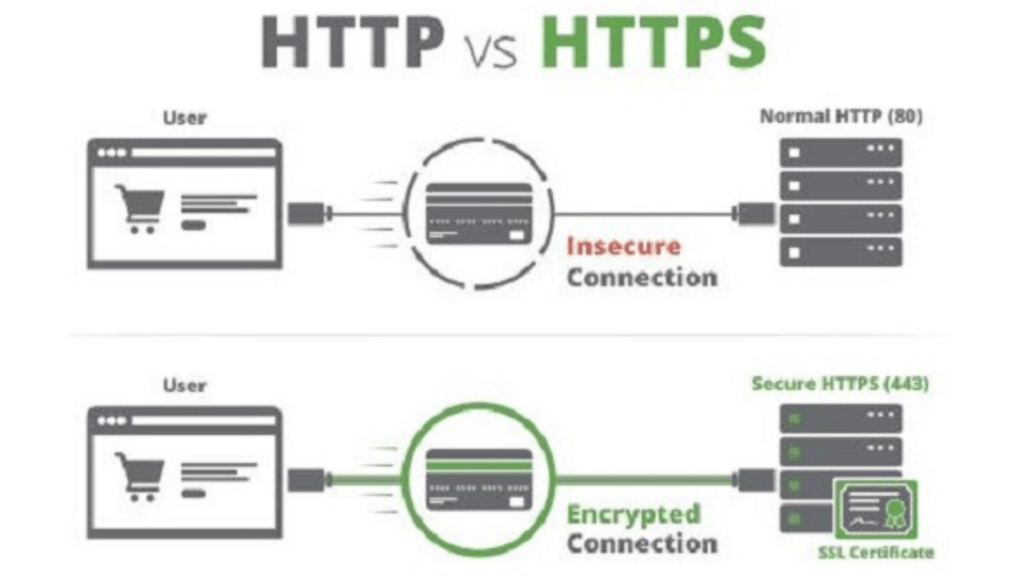
HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol, which allows different computer systems to communicate with each other. This protocol is used to transfer data from the webserver to a browser so that users can view web pages; the original protocol for early websites. While it's an efficient system for communication, it lacks security; with very little effort by the bad guys; communications can be breached between the browser and the server, and that’s not cool!
HTTPS is a modified version of the HTTP protocol with a layer of additional encryption. The -S identifies the site as secure because it has an SSL certificate that certifies the site’s ownership and encryption technology.
What Does HTTPS Mean?
The HTTPS protocol ensures a secure, encrypted 1:1 connection between browser and server.
The HTTP part means the same as above “Hyper Text Transfer Protocol, “ but the “S” at the end means so much more, the “S” means the site is secure with an SSL certificate.
Sites with SSL certificates use encryption to keep any connection to their site and any sensitive information such as your customers' credit card details, or account login information, secure.
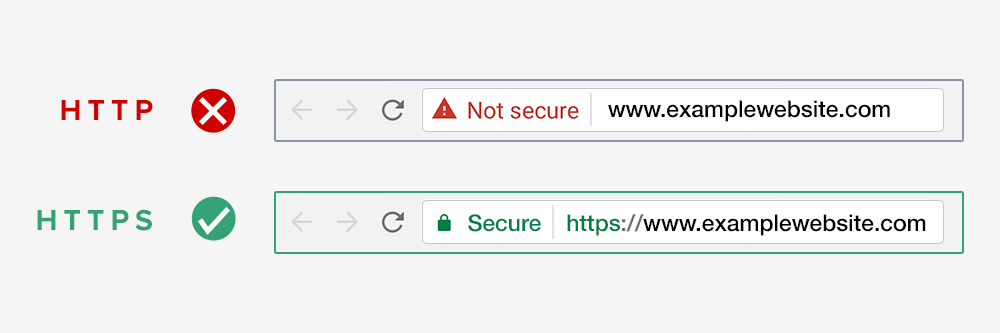
The HTTPS prefix is familiar to most people browsing the internet. Users can quickly identify whether a site uses HTTPS protocol by glancing at the URL in their web browser’s address bar.
Do not underestimate these security measures. Web-savvy online shoppers will not buy from untrustworthy sites. A secure SSL Certificate is crucial for websites to protect their users:
- credit card information
- business data
- personal information
- passwords, etc.
Another big reason to add SSL encryption for user security is the level of confidence and trust your customer will have for your site. Internet users have come to expect the https// prefix in their browser to be comfortable submitting any information or interacting with a website.
Gary Illyes, Google’s Webmaster Trends Analyst, affirmed this about secure sites in an interview:
How Does SSL Work?
When a browser visits a website, provided the site has an SSL certificate, the two begin a virtual handshake.
The first step of the SSL handshake, the browser checks the validity of the SSL certificate for authenticity.
Every SSL certificate has two keys, an associated public key, and a private key. Separately, their job is to handle encryption and decryption to communicate securely during the SSL handshake.
After the browser (the client) confirms the SSL certificate is valid, the client and website server create a third key, known as a session key. The session key is a symmetric key, used to secure the connection throughout the session.
The handshake is established in several hundred milliseconds to verify the client and server may communicate safely.
The Benefits of SSL Certificates:
More Reasons Why Securing your site with an SSL Certificate is a Smart Move:
- Your customer's data is encrypted and impossible to intercept.
- Your visitors can quickly see that you are the registered business and your domain is secure.
- Customers are more likely to trust and complete purchases from sites that use HTTPS
- You can use AMP - the technology behind mobile web browsers.
- Your site is secure it will not receive a penalty.
Issues Migrating to HTTPS:
- Google blocked from crawling the HTTP version of your site.
- Failure to update the test server and allow bots.
- Content duplication with both HTTPS and HTTP pages showing
- Improperly implemented redirects.
- Changing the entire structure/design while making the switch to HTTPS.
- Poor planning; poor implementation, or poor tracking.
Summary
Your website security is no longer something that only medical & financial institutions have to worry about. It has become equally important for all businesses and organizations to protect their information.
The SSL certificate allows visitors to know your site is credible, established, professional, and safe for them to engage or enter any information; secure or otherwise.
If you’re a business owner or an organization, your website address must meet the new standards with an “HTTPS” prefix to be search engine optimized for max performance.
Use a trusted source to migrate your site for you.
For those feeling intimidated by the prospect of switching to HTTPS no worries, it’s not as grueling or painful as it sounds, especially when it’s over and complete.
The security issue is not going away, putting this off is only going to cause more grief.
Let’s rip off the Band-Aid and prepare your site for the future once and for all!
Please let me know if that makes sense or you have further questions.
My best,
Leslie